Self-clinching studs are versatile, reliable fasteners designed to provide secure and permanent threaded connections in thin sheet materials. These fasteners are especially useful in applications where access to both sides of the material is restricted or where traditional fastening methods such as welding or tapping are impractical. By offering a simple yet effective method of creating threaded anchor points, self-clinching studs are widely used across various industries, including electronics, aerospace, automotive, and telecommunications.
In this article, we will discuss the material, surface treatment, classification, working principle, use method, and application scenarios of self-clinching studs.
1. Material Selection for Self-Clinching Studs
The material of a self-clinching stud plays a crucial role in determining its performance, durability, and application suitability. Common materials used for manufacturing self-clinching studs include:
Carbon Steel: A cost-effective material known for its strength, carbon steel is commonly used in automotive, industrial, and electronics applications. However, it requires surface treatment for corrosion resistance.
Stainless Steel: Known for its excellent corrosion resistance, stainless steel is often used in harsh environments, including aerospace, marine, and medical applications. It also provides superior strength, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications.
Brass: Brass is a popular choice for applications requiring good electrical conductivity, such as in electronics and telecommunications. It also offers corrosion resistance and ease of machining.
Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, aluminum is ideal for applications that require low weight and high resistance to environmental stress. It is commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and consumer electronics.
The choice of material depends on factors such as strength requirements, environmental exposure, weight considerations, and electrical conductivity needs.
2. Surface Treatment for Self-Clinching Studs
Surface treatment is essential for enhancing the performance and durability of self-clinching studs, particularly in terms of corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and overall aesthetic appearance. Several surface treatments can be applied to self-clinching studs, depending on the material and application environment:
Zinc Plating: Often applied to carbon steel self-clinching studs, zinc plating creates a protective barrier that resists corrosion. It is commonly used in automotive and industrial applications.
Nickel Plating: Nickel plating is used for stainless steel self-clinching studs to improve their corrosion resistance and provide a smooth, shiny finish. It is ideal for applications exposed to harsh chemicals or extreme weather conditions.
Anodizing: Used mainly for aluminum studs, anodizing increases surface hardness and improves corrosion resistance. It also allows for color customization, which can be important in consumer-facing products.
Passivation: This is commonly used for stainless steel to enhance its corrosion resistance by creating a protective oxide layer on the surface. It is particularly important in food processing, medical, and marine applications.
Phosphate Coating: Phosphate coatings are often used to provide lubrication for high-stress applications, reducing wear and improving the lifespan of the stud.
Surface treatments help to ensure that self-clinching studs can perform reliably in different environments, from industrial factories to marine and aerospace applications.
3. Classification of Self-Clinching Studs
Self clinching stud, also called self clinching bolt,self clinching screw. Is used to press riveting fasteners, standard parts.There are several main classifications:
Self clinching stud, the description mode is FH, stainless steel press riveting screw type is FHS, the material is SUS304.
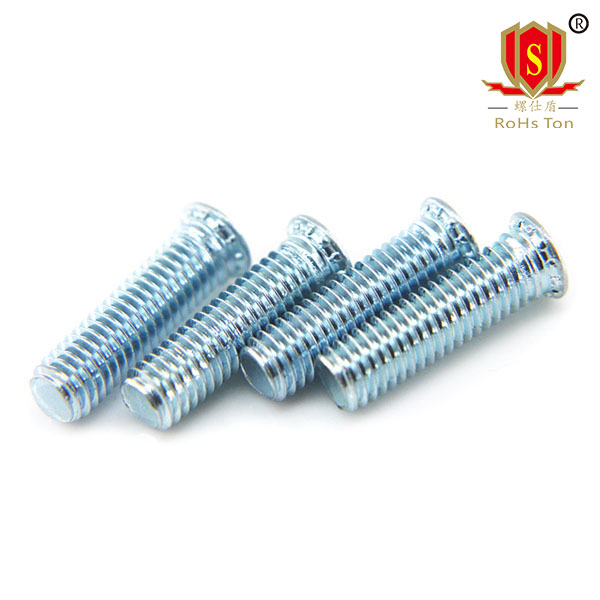


HFH series is a kind of high strength self clinching stud, compared with the conventional FH standard type self clinching stud, its head structure has been significantly strengthened, larger outside diameter, thickness and tooth pattern, effectively ensure high strength load.HFH: Basic type, heavy duty self clinching stud made of carbon steel 10B21. Heat treatment to HRC30~38, surface plating (preferred blue and white zinc), screw strength grade more than 8.8. Suitable for thin sheets below HRB85.

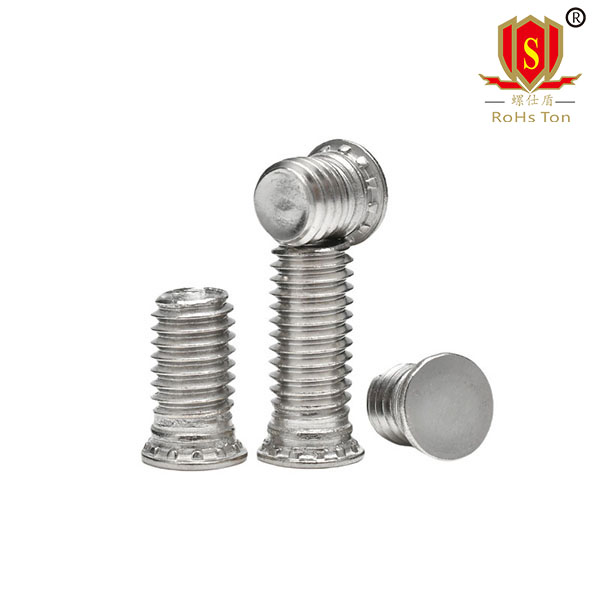
HFHS: Heavy duty self clinching stud made of stainless steel SUS304, suitable for thin sheets below HRB70. Aluminum plate copper plate is more commonly used.

HFH4: Heavy duty self clinching stud made of stainless iron SUS410, suitable for thin sheets below HRB95. Such as 304 stainless steel plate.HFHB: Heavy duty self clinching stud made of phosphor bronze material, often used in conductive environments, such as purple copper plate, plate hardness requirements less than HRB55.
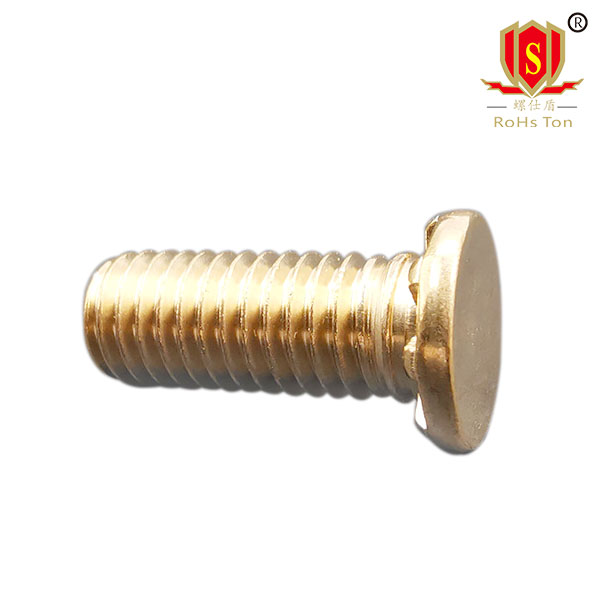

FHL small head carbon steel self clinching studs; FHLS small head stainless steel self clinching studs.Unlike the FH, the FHL series of self clinching studs is a lightweight type of self clinching stud with a smaller and thinner head, which is applied to thin sheets of no less than 1mmCompared with FH,FHL has smaller margin requirements.From the material is divided into FHL (carbon steel) and FHLS(stainless steel) two types.
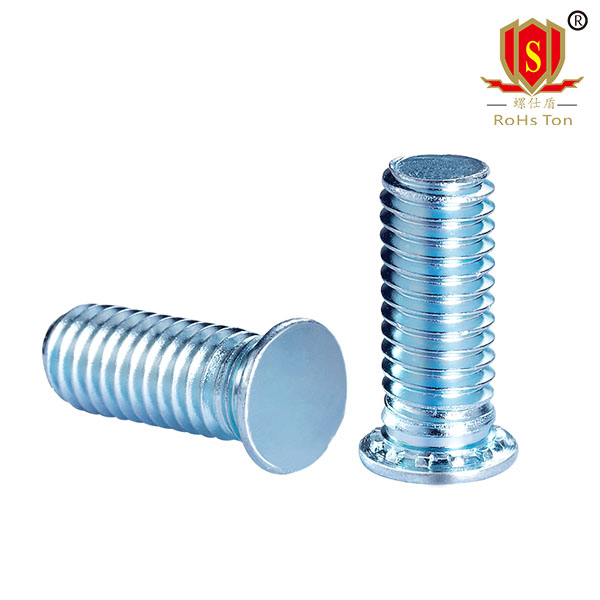
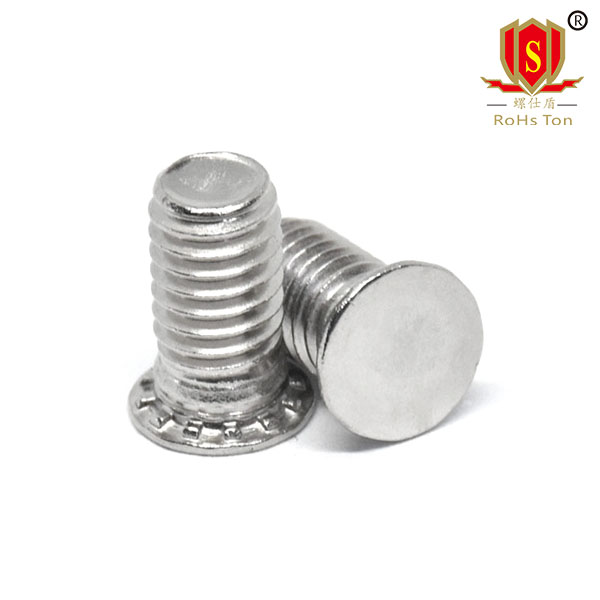


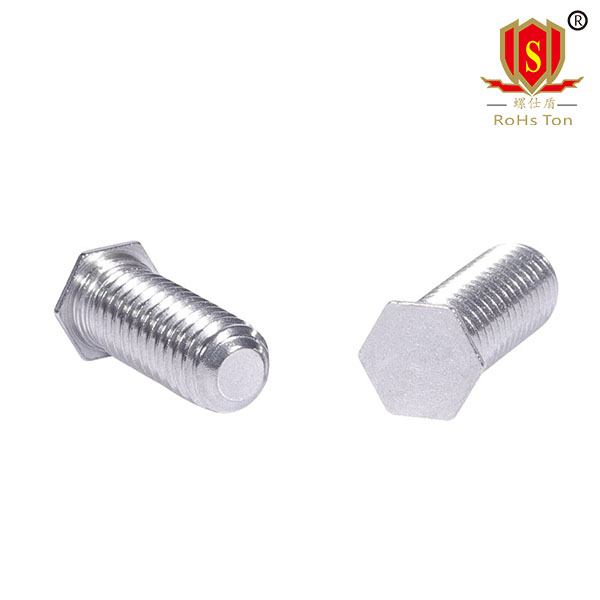
NFH hexagon self clinching studs and NFHS stainless steel hexagon self clinching studs are made by automatic lathe turning. The same as the round head self clinching stud, its use is into the round hole, the use of stamping riveting, so that the head can be tightly riveted in the thin plate, the plate thickness is not less than 0.5, less than 0.5mm special instructions, need to be customized.The difference between hexagonal head self clinching stud and round head is that hexagonal self clinching stud is completely dependent on the six opposite sides of the head stuck in the sheet metal to prevent sliding, and the production mode is directly turned by hexagonal rod, whose production cost and installation difficulty are higher than that of round head self clinching stud. Therefore, at present, hexagonal riveting screws are only used in some special cases, such as higher torque requirements.
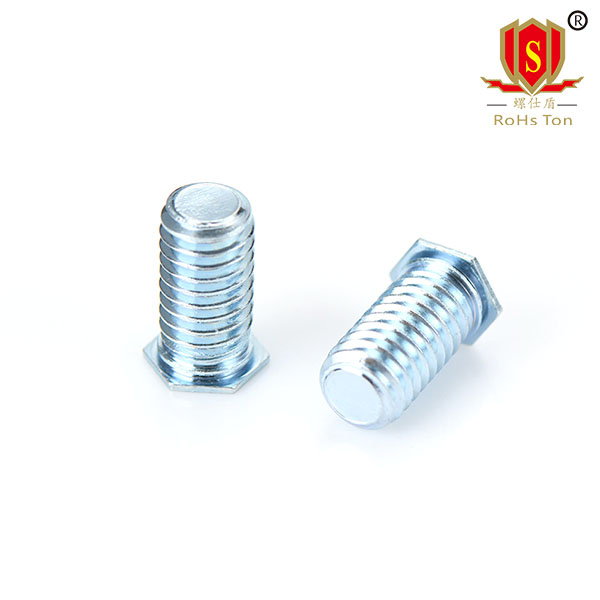


CHC countersunk head self clinching studs are suitable for riveting in milled blind holes and can withstand high loads. The hidden head allows the riveted joint to remain smooth even if the panel is fastened from the opposite side.Conventional FH type self clinching studs will leave a ring of marks on the riveted surface after installation (a ring of contact between the head of the stud and the plate, this kind of mark is a normal phenomenon), and it is not possible to completely remove the marks by grinding. In this case, the CHC type of countersunk head studs can be used to keep the back of the sheet completely flat.The CHA CHC type of stud solves the problem of sheet marking by milling out the flat bottom hole on one side of the sheet and pressing the countersunk screw into it.Unlike the installation conditions for FH type studs, the pre-set holes for CHA CHC type studs generally require milling and machining on the thin plate, such as punching slightly time-consuming.CHC type countersunk self clinching studs are made of stainless steel SUS303, aluminum 6061.Specifications can be produced: M3~M5(440~032).CHA, CHC type stud head thickness size is smaller, corresponding to a thinner plate.
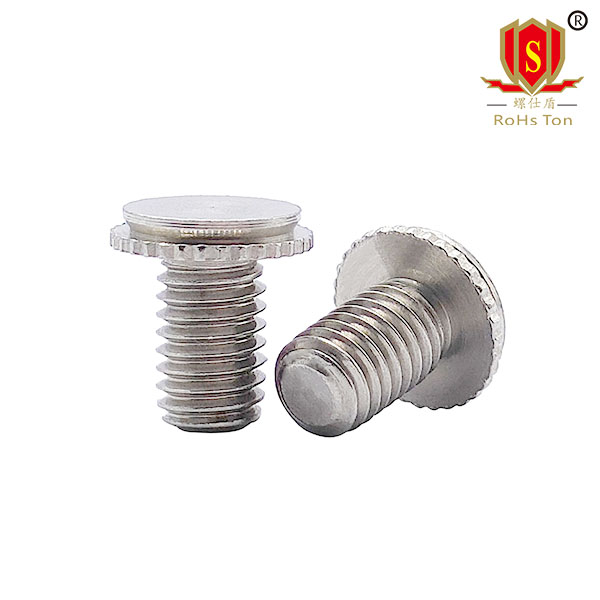


CFHA, CFHC stud head thickness size is larger, corresponding to a slightly thicker plate.
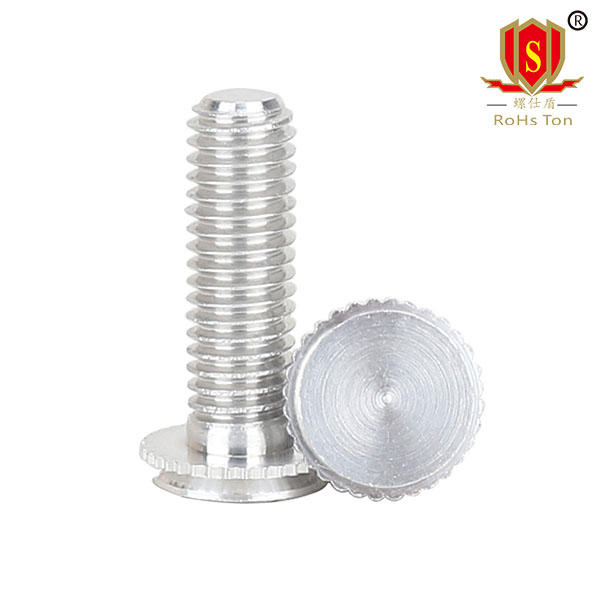
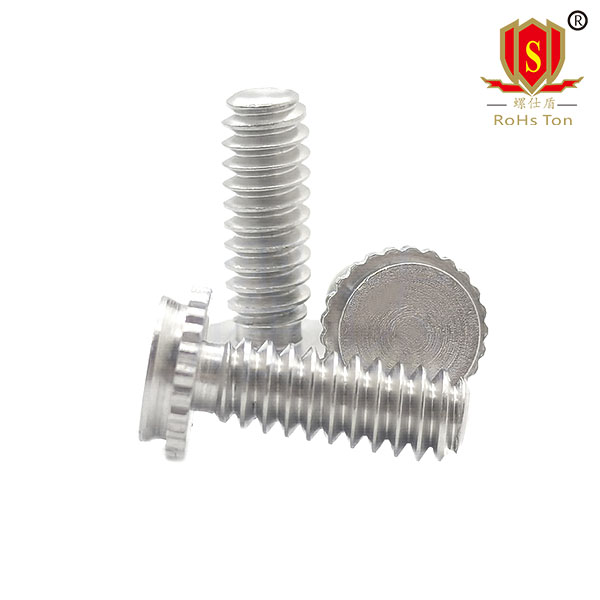


4. Working Principle of Self-Clinching Studs
The working principle of self-clinching studs is based on a mechanical locking mechanism that securely fastens the stud to thin sheet materials during installation. The process involves the following steps:
Insertion: The self-clinching stud is inserted into a pre-punched hole in the sheet material. The hole size is typically smaller than the outer diameter of the stud.
Clinching: Once inserted, the stud is subjected to pressure, which causes the flange at the rear of the stud to expand. The material around the hole is displaced, and the flange locks into place, forming a permanent connection between the stud and the sheet material. The clinching process creates a mechanical lock, preventing the stud from rotating or pulling out.
Threaded Connection: The stud's shaft is equipped with internal threads (or an unthreaded shaft can be threaded post-installation). Once the stud is secured in place, it provides a solid base for screws, bolts, or other fasteners to be installed, creating a reliable and durable threaded connection.
Self-clinching studs require no additional hardware like nuts, washers, or bolts, making them an efficient solution for fastening in thin sheet materials.
5. Use Method of Self-Clinching Studs
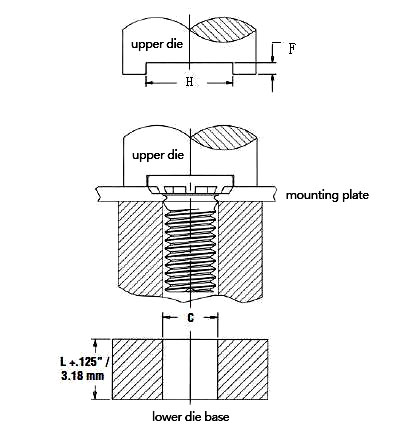
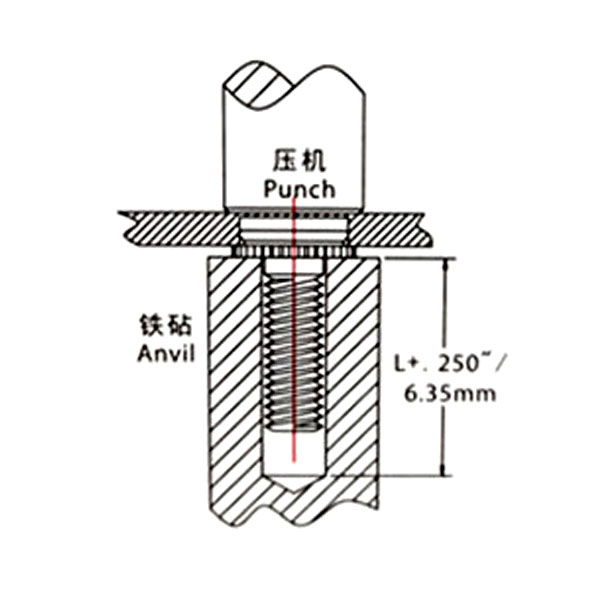
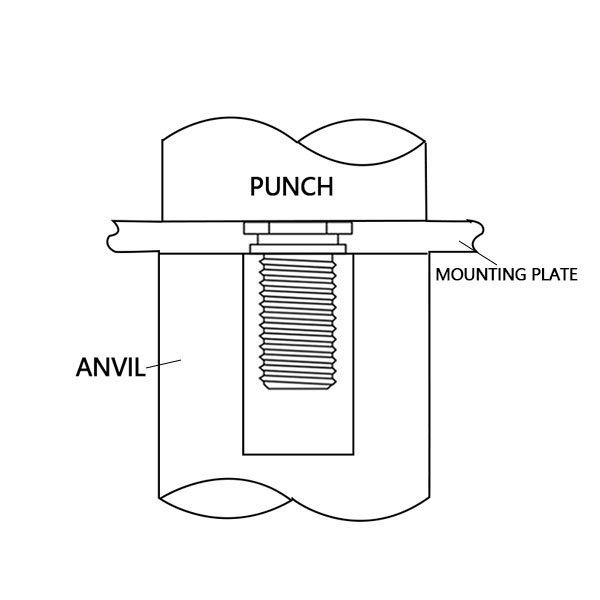
The use method for self-clinching studs is relatively simple, making them easy to install and highly efficient:
Step 1: Hole Preparation: The first step in using self-clinching studs is to prepare a hole in the sheet material. The hole should be slightly smaller than the stud’s diameter to allow for proper clinching. Hole size is typically specified by the manufacturer to ensure the correct fit.
Step 2: Insertion: Insert the self-clinching stud into the pre-punched hole. The stud is aligned so that the stud head against the material surface.
Step 3: Installation: Using a press or installation tool, apply force to the stud. The tool applies pressure to the stud, causing the plate material around the hole to squeeze into the gap between the stud head and the plate.. This clinching action creates a secure, permanent connection with the material.
Step 4: Threaded Fastening: Once the stud is installed, it is ready for use. You can now assemble the sheet with the other parts using nuts.
Self-clinching studs are typically installed using specialized tools such as hand tools, pneumatic presses, or automated machines for high-volume production.
6. Application Scenarios for Self-Clinching Studs
Self-clinching studs are used in a wide range of applications across various industries due to their versatility, strength, and ease of installation. Some of the common application scenarios include:
Electronics: Self-clinching studs are commonly used in electronics for securing components like circuit boards, connectors, and enclosures. Their ability to create a strong threaded connection in thin sheet metal makes them ideal for electronics enclosures and assemblies.
Aerospace: In aerospace, self-clinching studs are used to secure structural components, panels, and assemblies. The ability to withstand vibrations and high stresses makes them suitable for critical applications in aircraft and spacecraft.
Automotive: In the automotive industry, self-clinching studs are used for attaching parts like control panels, interior trim, and brackets. They are ideal for lightweight, durable fastenings that require a flush surface.
Telecommunications: Self-clinching studs are used in the telecommunications industry for securing racks, panels, and other equipment in data centers or communication systems.
Military: Military applications often require rugged, vibration-resistant fasteners for assembling equipment, vehicles, and protective casings. Self-clinching studs provide secure, reliable connections for high-performance systems.
Consumer Products: Self-clinching studs are also used in the production of consumer products like appliances, furniture, and recreational equipment, where secure fastenings are required but access to both sides of the material is limited.
Conclusion
Self-clinching studs offer a robust, efficient, and versatile fastening solution for thin sheet materials in a wide range of industries. With their ability to create permanent, vibration-resistant threaded connections without requiring access to both sides of the material, they provide significant advantages over traditional fastening methods like tapping, welding, or bolting. Whether used in electronics, aerospace, automotive, or telecommunications applications, self-clinching studs are an essential component for modern manufacturing processes. By understanding their materials, surface treatments, classification, working principles, installation methods, and applications, engineers and designers can choose the right type of self-clinching stud to meet the specific needs of their projects.




























