A Comprehensive Guide to Self-Clinching Nuts: Materials, Production Process, Heat Treatment, Surface Treatment, and More.
Self-clinching nuts are innovative fasteners designed for permanent installation in thin sheet materials, providing a strong and secure threaded connection without the need for additional hardware. This article explores the materials, production process, heat treatment, surface treatment, usage methods, scenarios, common models, and tips for choosing the right material and model when purchasing self-clinching nuts.
Materials
The choice of material for self-clinching nuts is critical, affecting their strength, corrosion resistance, and application suitability. Common materials include:
1.Steel: Known for high tensile strength and durability, often used in applications requiring robust fastening. It may be zinc plated for corrosion resistance.

2.Stainless Steel: Offers excellent resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for use in harsh environments, such as marine and chemical applications.

3.Aluminum: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, suitable for applications where weight savings are essential, such as in the aerospace industry.

4.Brass: Provides good corrosion resistance and conductivity, often used in electronic applications.

Production Process
The manufacturing process for self-clinching nuts generally involves several key steps:
1.Material Preparation: Metal sheets are selected and cut to size for forming.
2.Forming: The nuts are shaped using processes such as stamping or machining. Stamping is common for high-volume production, while machining allows for precise dimensions.
3.Thread Cutting: Internal threads are created, typically using tapping methods, allowing for the engagement with corresponding screws or bolts.
4.Heat Treatment: Certain materials undergo heat treatment to enhance mechanical properties, such as hardness and tensile strength.
5.Surface Treatment: After forming, a protective surface treatment may be applied to improve corrosion resistance and aesthetics.
Heat Treatment
Heat treatment enhances the mechanical properties of self-clinching nuts, particularly those made from steel. Common heat treatment processes include:
·
Annealing: Softens the material, improving ductility and reducing internal stresses.
·
Quenching and Tempering: Increases hardness and strength, especially in carbon steel nuts.
·
Aging: Used primarily for aluminum alloys to improve strength through precipitation hardening.
·
Surface Treatment
Surface treatment plays a significant role in the longevity and performance of self-clinching nuts. Common methods include:
·
Zinc Plating: A widely used method to provide corrosion resistance for steel nuts.
·
Anodizing: Enhances the natural oxide layer on aluminum, providing increased corrosion resistance and surface hardness.
·
Black Oxide: Offers a uniform, matte finish that provides mild corrosion resistance and reduces glare.
·
Use Method
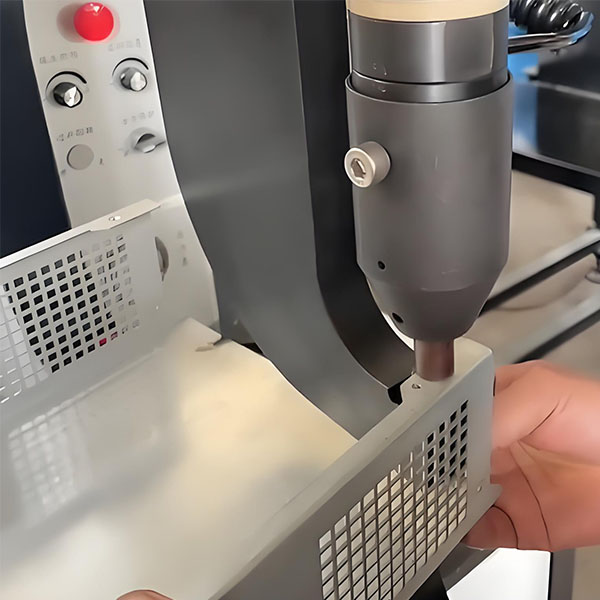
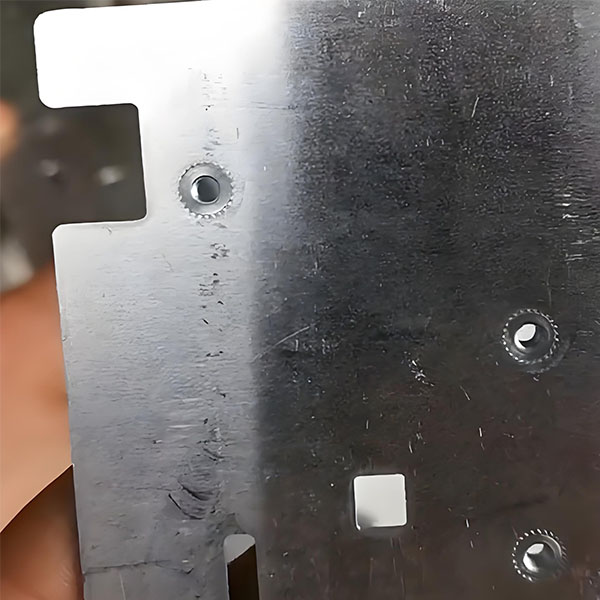
Self-clinching nuts are installed by pressing them into pre-drilled holes in sheet metal. The installation process typically involves:
1.Preparation: Clean the mounting surface to ensure it is free from debris.
2.Alignment: Position the nut over the pre-drilled hole, ensuring correct alignment.
3.Pressing: Use a hydraulic or pneumatic press to apply uniform pressure, embedding the nut into the sheet material until it is flush with the surface.
Use Scenarios
Self-clinching nuts are versatile fasteners used across various industries:
1.Electronics: Commonly used in electronic enclosures to secure circuit boards and components.
2.Automotive: Utilized in body panels and other components where strong, lightweight fasteners are essential.
3.Aerospace: Employed in aircraft structures, where weight and strength are critical considerations.
4.Industrial Equipment: Used in machinery and equipment for reliable assembly and ease of maintenance.
5.Consumer Products: Found in household appliances, furniture, and other goods for secure assembly.



Common Models
Several models of self-clinching nuts are available, each tailored for specific applications:
Standard Self-Clinching Nuts: Designed for general use in thin sheet materials.
Blind Self-Clinching Nuts: Ideal for applications where access to the back of the panel is restricted.
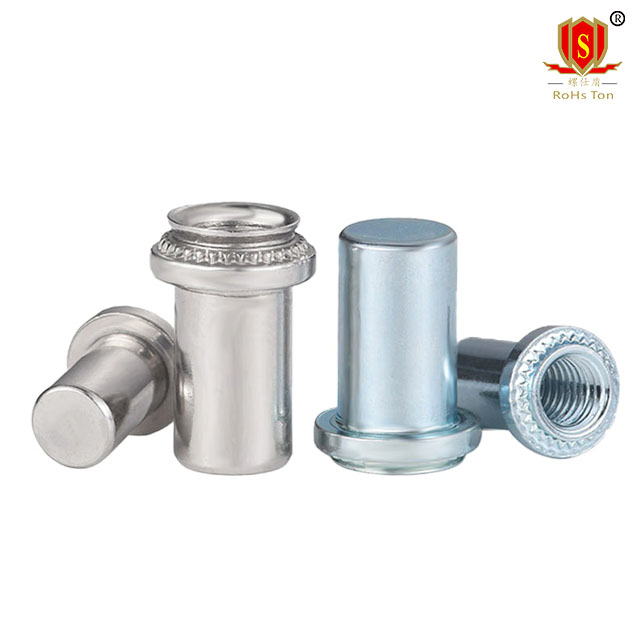
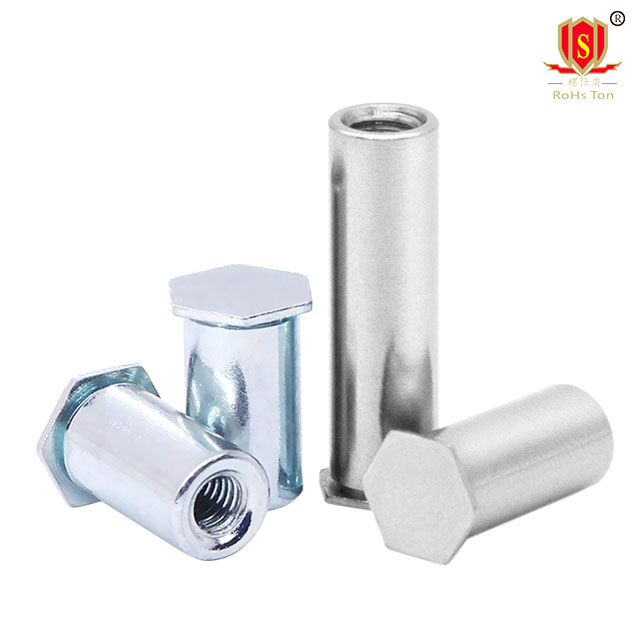


Locking Self-Clinching Nuts: Feature mechanisms to prevent loosening from vibrations, suitable for dynamic applications.
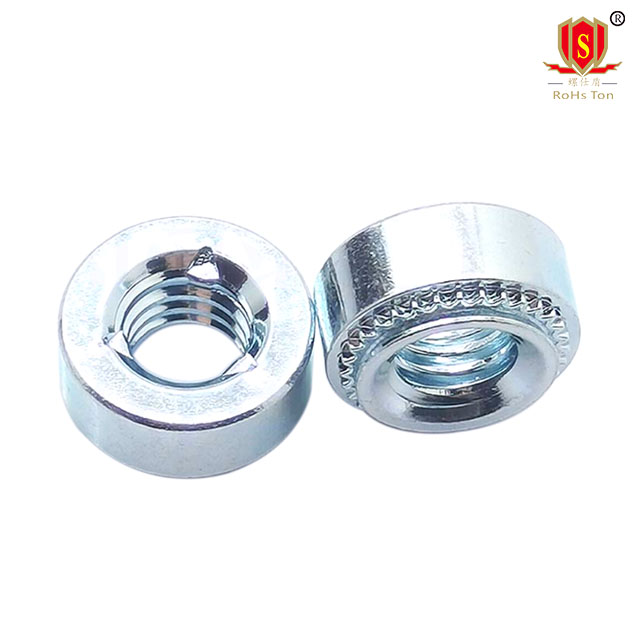

Recessed Self-Clinching Nuts: Allow for a flush finish, providing a clean look in assembled products.
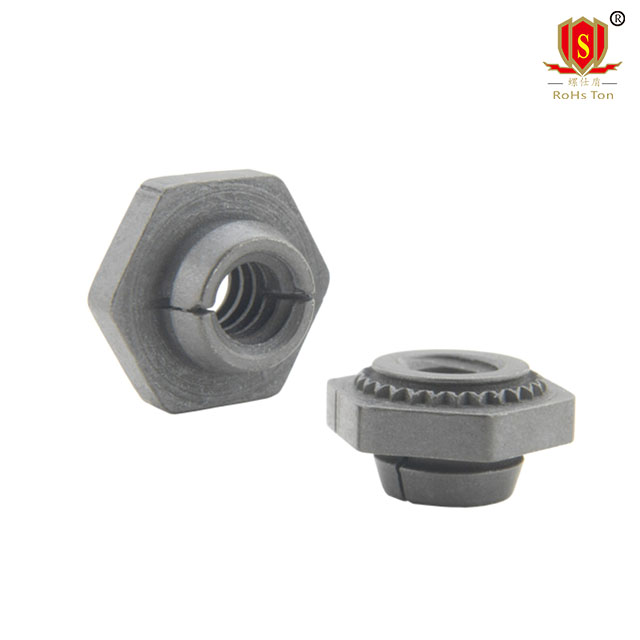

Choosing the Right Material and Model
When selecting self-clinching nuts, consider the following factors:
1.Application Requirements: Assess load-bearing capacity, environmental conditions, and specific requirements to determine the necessary material and strength.
2.Material Properties: Choose materials based on corrosion resistance, weight considerations, and mechanical properties. For outdoor or harsh environments, stainless steel or plated options may be preferable.
3.Nut Design: Select the appropriate model based on the installation method, access constraints, and desired aesthetics. Blind nuts are suitable for situations with limited access.
4.Installation Equipment: Ensure compatibility with available installation tools, as some nuts may require specialized equipment for proper installation.
5.Cost Considerations: Balance performance requirements with budget constraints. While higher-grade materials and features may incur a higher cost, they can provide long-term value and reliability.
Conclusion
Self-clinching nuts are essential components in modern manufacturing, providing strong, reliable, and efficient fastening solutions. Understanding their materials, production processes, heat and surface treatments, and usage methods enables manufacturers and engineers to make informed decisions. By carefully evaluating the factors involved in material and model selection, you can optimize your fastener choices for durability, performance, and cost-effectiveness.

























