Self-clinching standoffs are widely used fasteners designed to provide secure and reliable threaded connections in thin, soft, or brittle materials. These fasteners are particularly beneficial when you need to attach components to thin-walled panels or materials where traditional threading methods, such as tapping or welding, would be inefficient or impossible. Self-clinching standoffs provide a permanent, reliable solution for mounting and securing electronic components, panels, and enclosures. In this article, we will explore the material, surface treatment, classification, working principle, usage method, and common application scenarios of self-clinching standoffs.
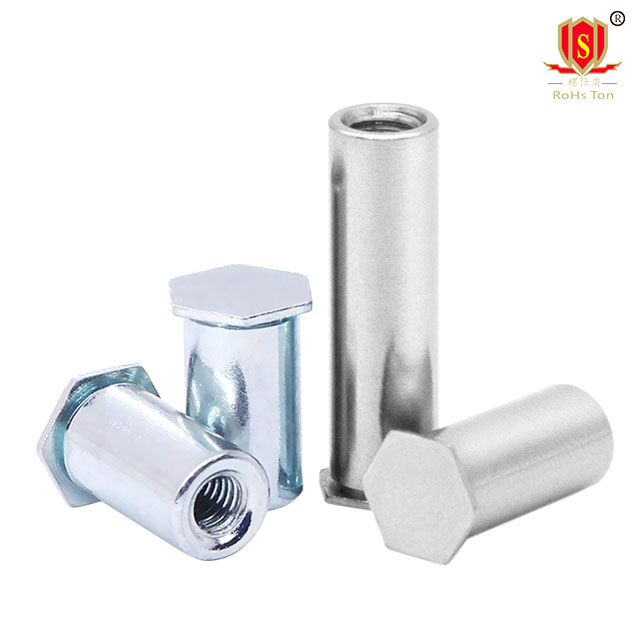

1. Material
The material chosen for self-clinching standoffs depends on the specific application requirements, such as strength, corrosion resistance, weight, and conductivity. Common materials used for manufacturing these fasteners include:
Carbon Steel: Offers high strength and is cost-effective, making it suitable for general industrial applications.
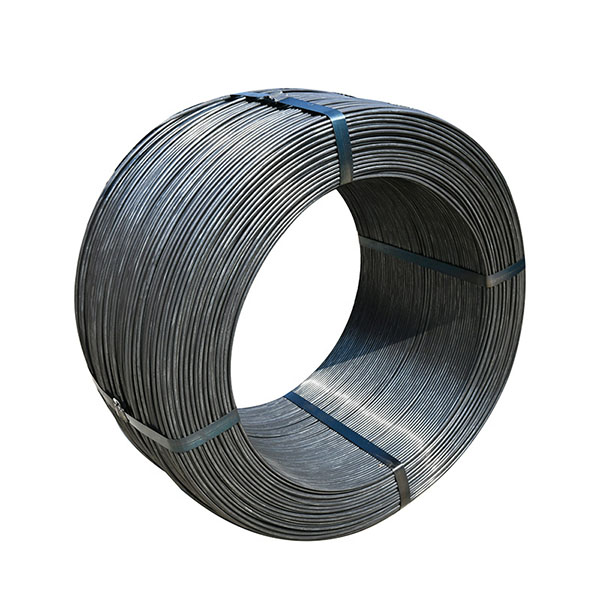

Stainless Steel: Known for its excellent corrosion resistance, stainless steel is commonly used in environments where the standoff will be exposed to moisture, chemicals, or high temperatures.
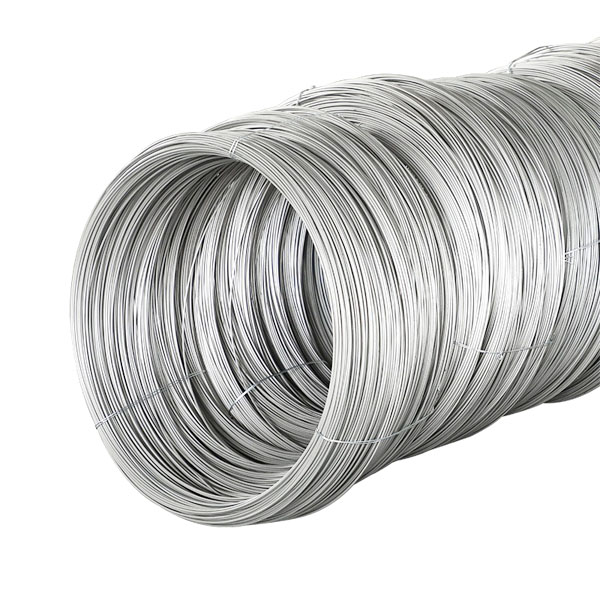

Aluminum: Lightweight and resistant to corrosion, aluminum is used in applications where reducing weight is important, such as in aerospace and automotive industries.
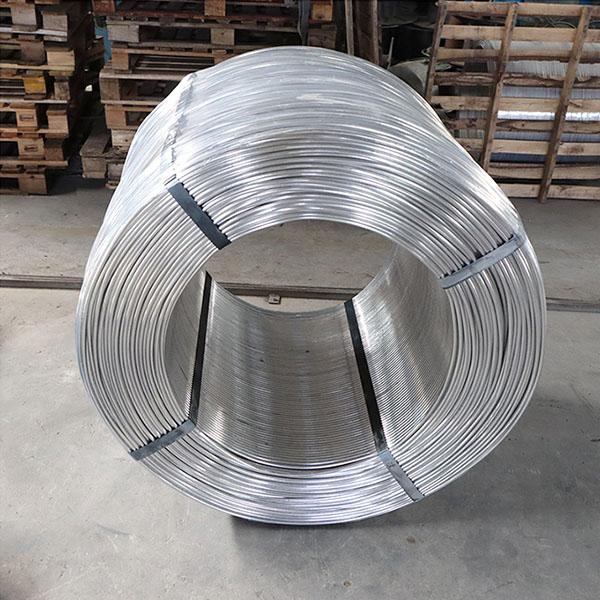

Stainless Iron: Good corrosion resistance and is suitable for specific stainless steel plates.

2. Surface Treatment
To enhance performance and increase the lifespan of self-clinching standoffs, surface treatments are often applied. The surface treatment protects the standoffs from wear, corrosion, and environmental factors. Common surface treatments include:
Zinc Plating: A common treatment for carbon steel self clinching standoffs, zinc plating provides corrosion resistance by forming a protective layer on the surface of the standoff.
Nickel Plating: Nickel-plated self clinching standoffs offer enhanced corrosion resistance, improved wear resistance, and an aesthetically appealing finish. It is commonly used in harsh environments.
Anodizing: Applied to aluminum self clinching standoffs, anodizing creates a protective oxide layer that increases corrosion resistance and provides the option for colored finishes.
Phosphate Coating: Often applied to steel self clinching standoffs, phosphate coatings help to reduce friction and improve the performance of the fastener.
Passivation: This treatment is used for stainless steel self clinching standoffs to enhance the natural corrosion resistance by removing contaminants from the surface and promoting the formation of a stable oxide layer.
Surface treatments are selected based on the intended application, environmental factors, and the material of the standoff.
3. Classification
Self-clinching standoffs can be classified in various ways depending on their design, material, and the thread type. The main classifications include:
By Design:
Blind Self-Clinching Standoffs: Blind hole self clinching standoff are closed at one end and open at the other. There are four types: BSO, BSOS, BSO4 and BSOA.Suitable for scenarios where water or oil resistance is required.
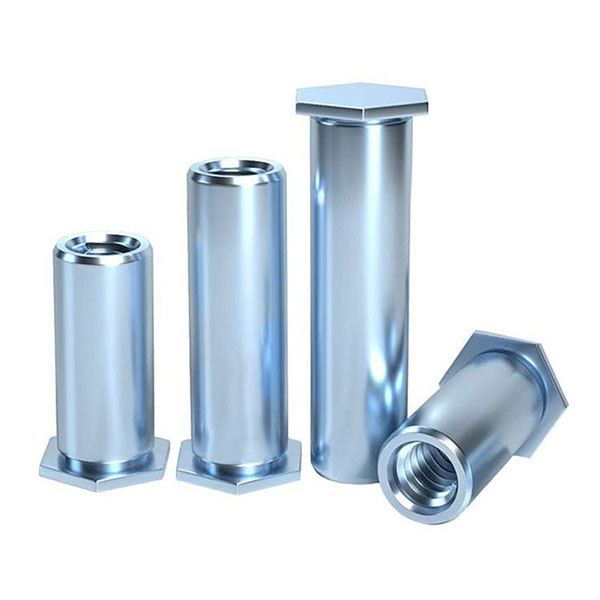

Through Hole Self Clinching Standoffs: Both ends of the through hole self clinching standoff are open, and the hollow inner wall is threaded. There are eight types: SO, SOS, SO4, SOA, SOO, SOOS, SOO4 and SOOA.
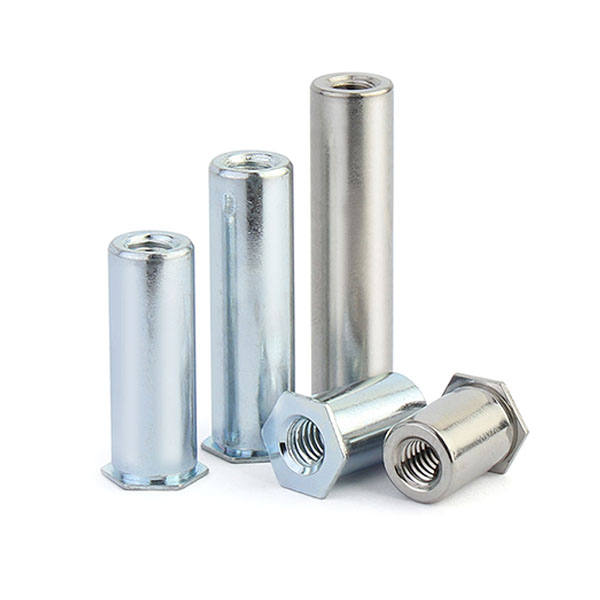

By Thread Type:
Ordinary Thread Self Clinching Standoff: Only part of their hollow inner wall is tapped out of the thread, there are SO, SOS, SO4, SOA, BSO, BSOS, BSO4, BSOA eight types.
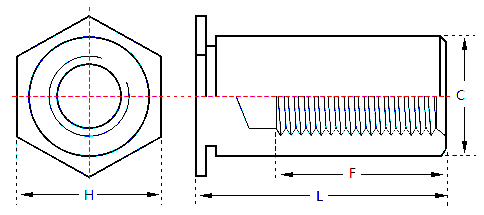
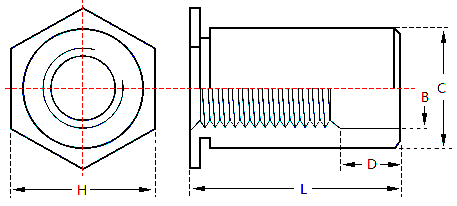
Full Thread Self Clinching Standoff: Their hollow inner walls are all threaded to provide higher fastening force. There are four types: SOO, SOOS, SOO4 and SOOA.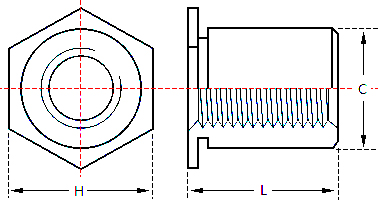
By Installation Method:
Stainless Steel Self Clinching standoff: SOS,BSOS,SOOS.
Carbon Steel Self Clinching Standoff: SO,BSO,SOO.
Stainless Iron Self Clinching Standoffs: SO4,BSO4,SOO4.
Aluminum Self Clinching Standoffs: SOA,BSOA,SOOA.
4. Working Principle
Self Clinching Standoff have a hexagonal shape at one end and a cylindrical shape at the other end, with a groove in the middle of the hexagonal edge and the cylindrical shape. The working principle of the self clinching standoff is to press one end of the stud into a pre-set hole in a thin plate by a press, so that the periphery of the hole is plastically deformed, and the deformed portion is squeezed into the groove of the self clinching standoff, so that the self clinching standoff is fastened to the thin plate to form an effective internal thread. This fastening method eliminates the need for pre-tapping, simplifies the installation process, and provides a reliable structural connection.
5. Use Method
The use of self-clinching standoffs is straightforward and involves the following steps:
Preparation: A hole is drilled or punched in the material (typically a thin metal sheet, panel, or enclosure) that is the same diameter or slightly smaller than the outer diameter of the standoff.
Insertion: The self-clinching standoff is inserted into the hole from one side of the material.
Clinching: The standoff is pressed or clinched into place using a press tool, which deforms the edges of the standoff and locks it into the material.
Threaded Connection: Once the standoff is securely in place, screws or bolts can be inserted into the internal threads of the standoff, providing a stable attachment point for other components.
The installation of self-clinching standoffs is fast and does not require additional processes such as welding or tapping, making them highly efficient for high-volume production environments.
6. Application Scenarios
Self-clinching standoffs are used in a wide range of industries where secure, reliable threaded connections are needed in thin or soft materials. Some common application scenarios include:
Electronics and Electrical Equipment:
PCB Mounting: Self-clinching standoffs are often used to mount printed circuit boards (PCBs) inside electronic enclosures or housings. The standoffs provide a secure, vibration-resistant connection for PCB screws or other components.
Power Supply Units: Used to elevate components such as transformers and capacitors off the surface, preventing short circuits and providing better heat dissipation.
Automotive Industry:
Used in the assembly of automotive components, such as dashboards, control panels, and engine components, where secure mounting and vibration resistance are crucial.
Aerospace:
Telecommunications:
Industrial Equipment:
Self-clinching standoffs are used in the assembly of various industrial machines, including electrical panels, control cabinets, and automated machinery.
Medical Devices:
Used for the secure mounting of components in medical equipment, such as displays, control boards, and housings, where precision and reliability are essential.
Conclusion
Self-clinching standoffs are essential components for applications requiring secure threaded connections in thin, soft, or brittle materials. Their material versatility, simple installation process, and ability to withstand vibration and mechanical stress make them ideal for a wide range of industries, from electronics to automotive and aerospace. With the right material, surface treatment, and proper installation, self-clinching standoffs provide a reliable, cost-effective solution for mounting and securing components in a variety of environments.























